| [1] Klein KB, Stafinski TD, Menon D. Predicting survival after liver transplantation based on pre-transplant MELD score: a systematic review of the literature. PLoS One. 2013;8(12): e80661.
[2] Alex Bishop G, Bertolino PD, Bowen DG, et al. Tolerance in liver transplantation. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2012;26(1):73-84.
[3] Xie XJ, Ye YF, Zhou L, et al. Th17 promotes acute rejection following liver transplantation in rats. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2010;11(11):819-827.
[4] Stefanidis C, Callebaut G, Ngatchou W, et al. The role of biventricular assistance in primary graft failure after heart transplantation. Hellenic J Cardiol. 2012;53(2):160-162.
[5] Casas-Melley AT, Falkenstein KP, Flynn LM, et al. Improvement in renal function and rejection control in pediatric liver transplant recipients with the introduction of sirolimus. Pediatr Transplant. 2004,8(4):362-366.
[6] Dong JY, Yin H, Li RD, et al. The relationship between adenosine triphosphate within CD4(+) T lymphocytes and acute rejection after liver transplantation. Clin Transplant. 2011;25(3):E292-E296.
[7] Hashimoto K, Miller C, Hirose K, et al. Measurement of CD4+ T-cell function in predicting allograft rejection and recurrent hepatitis C after liver transplantation. Clin Transplant. 2010;24(5):701-708.
[8] Sun Y, Yin S, Xie H, et al. Immunophenotypic shift of memory CD8 T cells identifies the changes of immune status in the patients after liver transplantation. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2009;69(7):789-796.
[9] Gerlach UA, Vogt K, Schlickeiser S, et al. Elevation of CD4+ differentiated memory T cells is associated with acute cellular and antibody-mediated rejection after liver transplantation. Transplantation. 2013,95(12):1512-1520.
[10] Kubota N, Sugitani M, Takano S, et al. Correlation between acute rejection severity and CD8-positive T cells in living related liver transplantation. Transpl Immunol. 2006,16(1): 60-64.
[11] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30.
[12] Rang JH, Zhang SN, Liu J, et al. Improvements of Orthotopic Liver Transplantation Model in Rhesus Monkey. Zhongguo Puwaijichu yu Linchuang Zazhi. 2010;17(7):694-698.
[13] Rang JH, Li Z, Liu J, et al. Construction of stable rhesus monkey orthotopic liver transplantation models using two-cuff technique. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiun yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(5):762-768.
[14] Solez K. History of the Banff classification of allograft pathology as it approaches its 20th year. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2010;15(1):49-51.
[15] Demetris A, Adams D, Bellamy C, et al. Update of the international banff schema for liver allograft rejection: working recommendations for the histopathologic staging and reporting of chronic rejection. An International Panel. Hepatology. 2000;31(3):792-799.
[16] Alcher A, Hayden LM, Brady WA, et al. Characterization of human inducible costinulator ligand expression and function. J Immunol. 2000;164(9):4689-4696.
[17] Coyle AJ, Gutierrez-Ramos JC. The expanding B7 superfamily increasing complexity in costinulatory signals regulating T cell function. Nat Immunol. 2001;2(3):203-209.
[18] Tafuri A, Shahinian A, Bladt F, et al. ICOS is essential for effective T-helper-cell responses. Nature. 2001;409(6816): 105-109.
[19] Coyle AJ, Lehar S, Lloyd C, et al. The CD28-related molecule ICOS is required for effective T cell-dependent immune responses. Immunity. 2000;13(1):95-105.
[20] Engelhard VH. Structure of peptides associated with class I and class II MHC molecules. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994; 12:181-207.
[21] MacNamara A, Kadolsky U, Bangham CR, et al. T-cell epitope prediction: rescaling can mask biological variation between MHC molecules. PLoS Comput Biol. 2009;5(3): e1000327.
[22] Stranzl T, Larsen MV, Lundegaard C, et al. NetCTLpan: pan-specific MHC class I pathway epitope predictions. Immunogenetics. 2010;62(6):357-368.
[23] Ossevoort MA, De Bruijn ML, Van Veen KJ, et al. Peptide specificity of alloreactive CD4 positive T lymphocytes directed against a major histocompatibility complex class-I disparity. Transplantation. 1996;62(10):1485-1491.
[24] Kovalik JP, Singh N, Mendiratta SK, et al. The alloreactive and self-restricted CD4+ T cell response directed against a single MHC class II/peptide combination. J Immunol. 2000; 165(3):1285-1293.
[25] Mendiratta SK, Kovalik JP, Hong S, et al. Peptide dependency of alloreactive CD4+ T cell responses. Int Immunol. 1999;11(3):351-360.
[26] Casares S, Bona CA, Brumeanu TD. Modulation of CD4 T cell function by soluble MHC II-peptide chimeras. Int Rev Immunol. 2001;20(5):547-573.
[27] Sadegh-Nasseri S, Dalai SK, Korb Ferris LC, et al. Suboptimal engagement of the T-cell receptor by a variety of peptide-MHC ligands triggers T-cell anergy. Immunology. 2010;129(1):1-7.
[28] Mirshahidi S, Huang CT, Sadegh-nasseri S. Anergy in peripheral memory CD4(+) T cells induced by low avidity engagement of T cell receptor. J Exp Med. 2001;194(6): 719-731.
[29] Choi S, Schwartz RH. Molecular mechanisms for adaptive tolerance and other T cell anergy models. Semin Immunol. 2007;19(3):140-152.
[30] Schwartz RH. T cell anergy. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21: 305-334.
[31] Coutinho A, Caramalho I, Seixas E, et al. Thymic commitment of regulatory T cells is a pathway of TCR-dependent selection that isolates repertoires undergoing positive or negative selection. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005;293:43-71.
[32] Chen W, Murphy B, Waaga AM, et al. Mechanisms of indirect allorecognition in graft rejection: class II MHC allopeptide-specific T cell clones transfer delayed-type hypersensitivity responses in vivo. Transplantation. 1996; 62(6):705-710.
[33] Slavcev A. Mechanisms of allorecognition and organ transplant rejection. Ann Transplant. 2001;6(4):5-8.
[34] Fujio K, Okamura T, Sumitomo S, et al. The functions of CD4+CD25-LAG3+ regulatory T cells and Egr2 in the regulation of autoimmunity. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2014;37(2):69-73.
[35] Wilczynski JR, Radwan M, Kalinka J. The characterization and role of regulatory T cells in immune reactions. Front Biosci. 2008;13:2266-2274.
[36] Shiao SL, Mcniff JM, Pober JS. Memory T cells and their costimulators in human allograft injury. J Immunol. 2005; 175(8):4886-4896.
[37] Vu MD, Clarkson MR, Yagita H, et al. Critical, but conditional, role of OX40 in memory T cell-mediated rejection. J Immunol. 2006;176(3):1394-1401.
[38] Vu MD, Amanullah F, Li Y, et al. Different costimulatory and growth factor requirements for CD4+ and CD8+ T cell-mediated rejection. J Immunol. 2004;173(1):214-221.
[39] Porrett PM, Lee MK 4th, Lian MM, et al. A direct comparison of rejection by CD8 and CD4 T cells in a transgenic model of allotransplantation. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2008;56(3):193-200.
[40] Youssef AR, Otley C, Mathieson PW, et al. Role of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in murine skin and heart allograft rejection across different antigenic desparities. Transpl Immunol. 2004;13(4):297-304. |
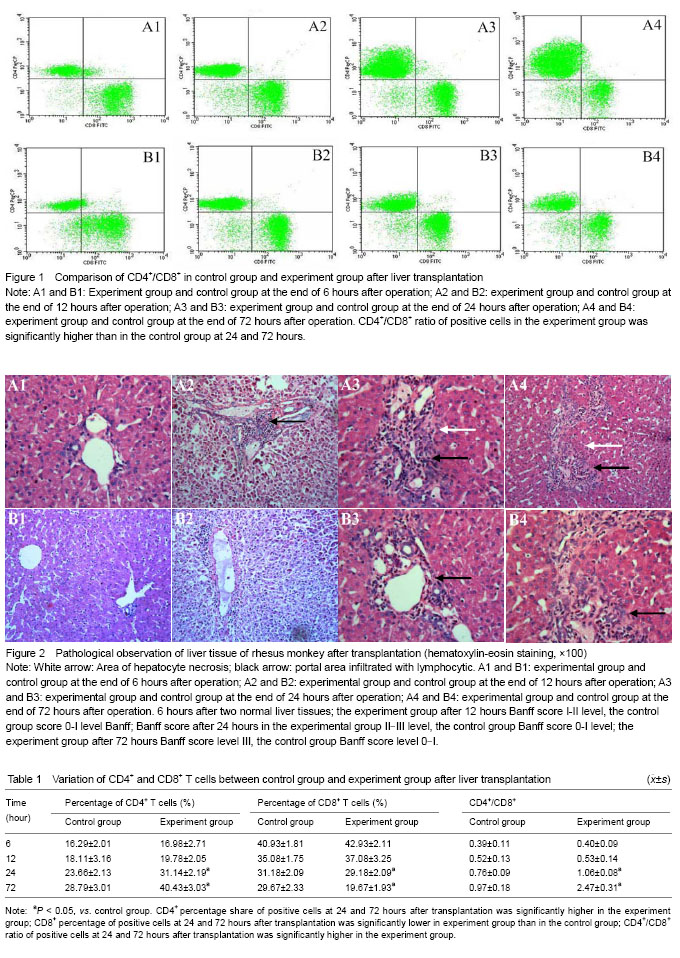
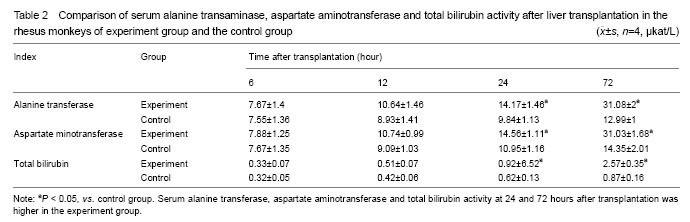
.jpg)